Chmod Example Directory
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
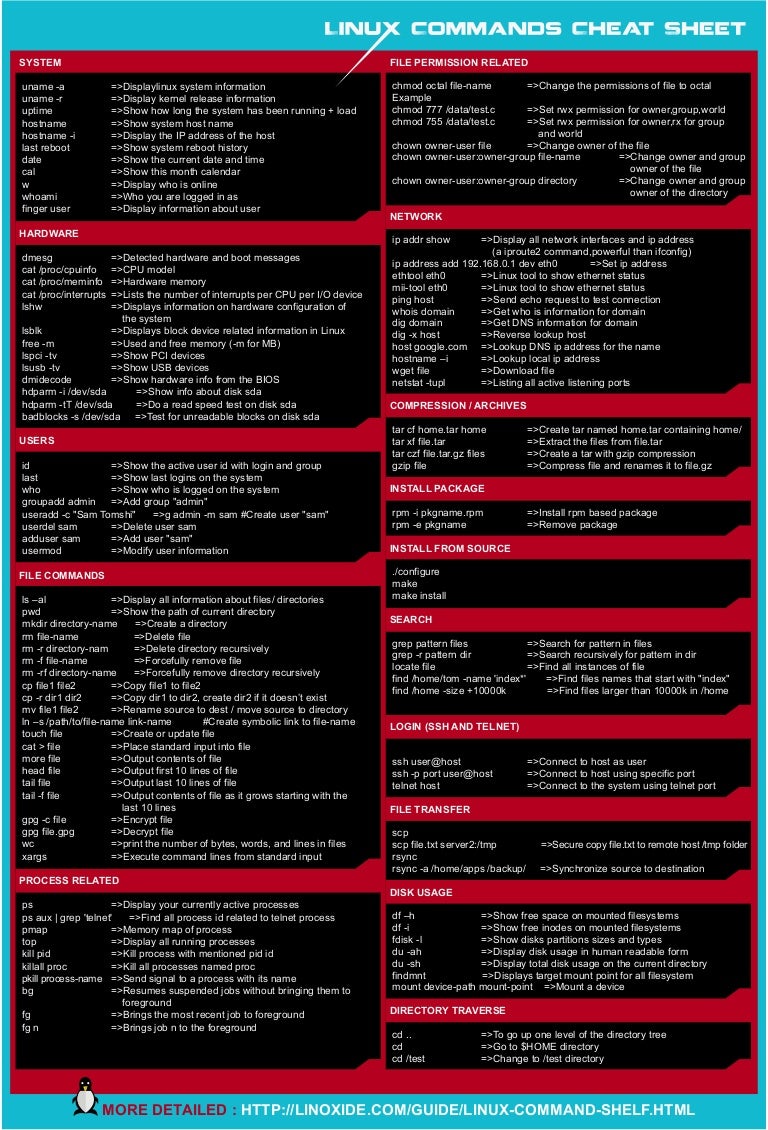
Linux Cheat Sheet

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Change File Directory Permission Using Chmod And Chown In Ubuntu Linux
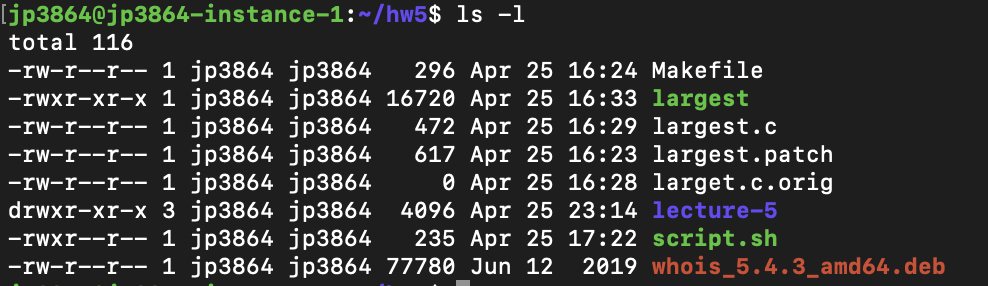
Chmod Jessica Peng

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
If you specify the -h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change.

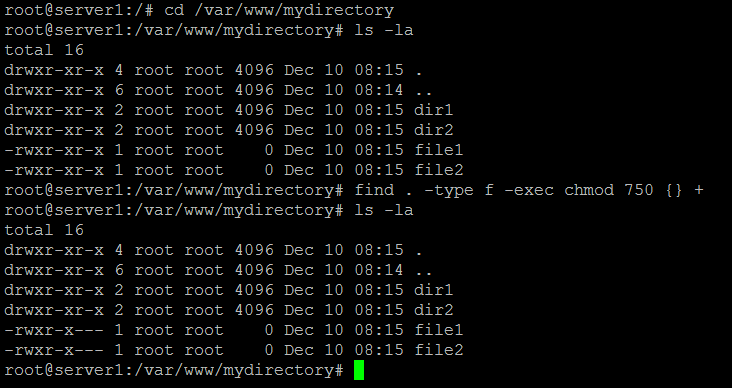
Chmod example directory. W3Schools is optimized for learning, testing, and training. -type f -exec chmod 750 {} +. Sudo chmod XXX -R directory-location You can also simply navigate to the folder (Using cd command) where you want to apply the permissions to all of the folder contents and run the following command.
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command. After changing a directory's mode to 775 the folder's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:.
Removing execute permissions to a user. Chmod -R 755 /var/www/html. You can use the numbers instead of the letters in chmod, like this:.
Arbitrary code from (sometimes) arbitrary fora pasted into arbitrary terminals, by a guy who wants to "chmod 707 -Rv ." except for two directories sourced from "some guy" with 2 posts?. This next one will set the group’s write permission on directory and all its content recursively. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:.
Add write permission (w) to the Group's (g) access modes of a directory, allowing users in the same group to add files:. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. Examples chmod 644 file.htm.
One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. Chmod ugo+x myfile - Same as the above command, but specifically specifies user, group and other.
To change the permissions of a directory, we run:. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755. In assgn1_client.c, has owner’s permission as rw-, which means the owner mik can only read(r) and write(w) the file but cannot execute(x).
Chmod +hrs sysfile sets the hidden, read-only, and system attributes for sysfile. $ chmod 755 -R directory_name $ chmod 755 -R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation. The command chmod can be followed by the “options” element which allows further options of the chmod command to be defined.The element “mode” represents the so-called umask that is applied to the “file” (which can also be a directory).This mask contains the information responsible for determining whether or not a user class should receive new access rights or be removed of the.
To modify the permissions of each and every file and folder in a provided directory at once, use sudo chmod with -R:. For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use:. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;.
Changing permission to a single set. It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. This sets the permissions to.
Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. It will report only on changes. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command.
After changing a directory's mode to 644 the folder's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:. 7 Chmod Command Examples for Beginners 1. The verbose option will cause chmod to report on the action.
I hope this article has helped you in applying the chmod command to a folder and all of its contents. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. Chmod --changes|-c {--recursive|-R} {PATH}.
Adding execute permissions to others. These examples are extracted from open source projects. Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure.
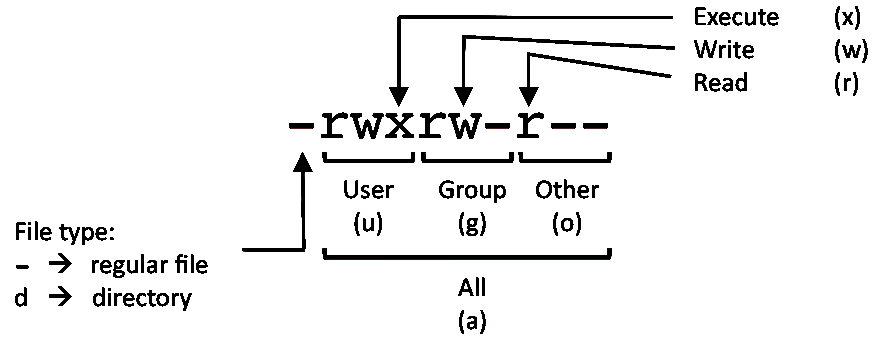
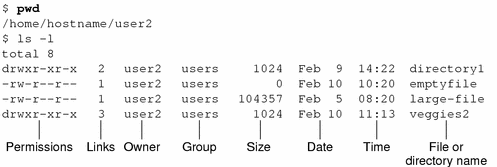
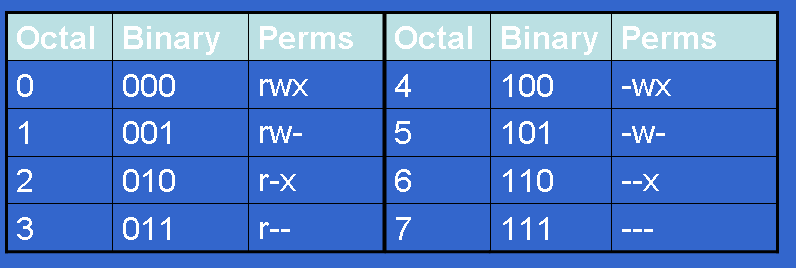
In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. $ chmod 604 filename Umask 022 is Responsible for the default permission of a file. Chmod syntax for symbolic values chmod OPTION MODE1,MODE2 FILE.
In the next post we will see more about chmod options and examples such as change file/folder permissions recursively, SUID, SGID and Sticky bit. The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value. Following is a sample of ls -l command output.
From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. $ chmod 644 filename. Chmod -cR g+w /path/to/directory.
Chmod options-R – Recursively change the permissions in the file under the directory. Perform chmod recursive with -R or --recursive. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
Explore your self on how to use other options. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. Save yourself the effort with.
+ symbol means adding permission. This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal:. Add multiple permission to a file/directory.
Examples Using chmod # Below are examples of making changes to permissions:. Current permission on these files can be checked by using ls -lrt example/ command as shown below. Chmod a=rwx file turns on read, write, and execute permissions, and turns off the hidden, archive, and system attributes.
If you specify both the -h flag and the -R flag, the chmod command descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link is encountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is not changed. The first set three letters after the file type tell what the Owner of the file, have permissions to do. Add single permission to a file/directory.
This can be done as follows:. Read by owner only $ chmod 400 sample.txt Read by group only $ chmod 040 sample.txt Read by anyone $ chmod 004 sample.txt Write by owner only. If you want to change all the permissions inside a directory, you can change them for every file by hand — which can take a very long time.
Sudo chmod 644 filename-or-full-filepath. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE…. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and basic understanding.
You may check out the related API usage on the sidebar. The following are 30 code examples for showing how to use os.chmod(). Group can read only;.
To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute):. Sudo chmod 777 Directory /* We can see the following output which clearly reflects the change in file permissions:. Chmod examples using octal mode :.
This next example will apply read/write permission to file for the owner. D rw-r--r-- Popular CHMOD Commands (TOP ) chmod 777. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.
Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma). $ chmod 540 filename. Chmod -v u+rw /path/to/file.
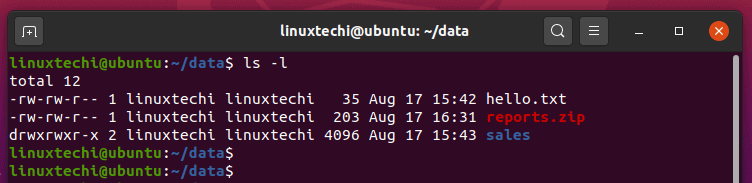
For a directory, the permissions govern who can cd into the directory and who can create, or modify files within the directory. In this example we have a directory called example which contains two files hello.rs and hello. If you want to recursively the change the permission of all the files in a directory then you need to use -R option with chmod command.
To remove permission from any file/directory you have to use “–” Symbol. Directory where d represents a directory and – represents a normal file. Examples of Using chmod command Assign permission to a File.
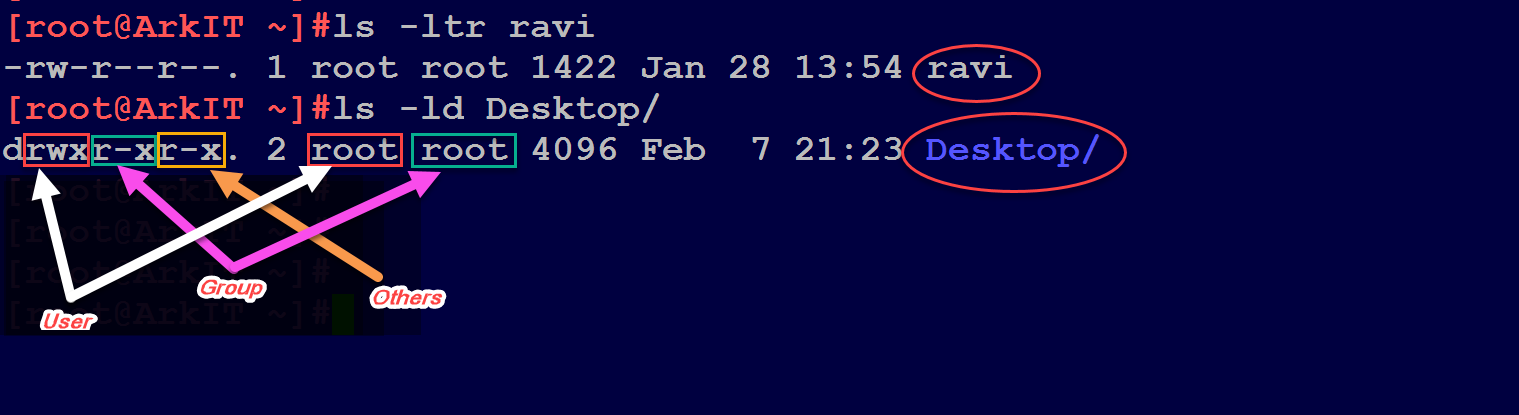
To see what permissions have been set on a file or directory, we can use ls. Chmod command Example 6:. Chmod u+x myfile - Gives the user execute permission on myfile.;.
For example, give read, write ( 4 + 2 = 6 ) to user and nothing ( 0 ) to group, and read ( 4 ) to others. You can vote up the ones you like or vote down the ones you don't like, and go to the original project or source file by following the links above each example. Another way of assigning permissions is by using the text notation.
Others can read only". For example, give read, execute ( 4 + 1 = 5 ) to user and read (4 ) to group, and nothing ( 0 ) to others. Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions.
In this section we will show you how to change permissions on directory and sub-directories with examples. Let’s give Read and Write permission to User/Owner using chmod command. In this method, the chmod command takes flags or symbols which represent the owner, group, others or all users ( u, g , and o) in the syntax.
(or access for directories) (x), execute only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user (X), set user or group ID on execution (s), sticky (t), the. D rwxrwxr-x Popular CHMOD Commands (TOP ) chmod 777. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write.
Sudo find directory -type d/f -exec chmod privilege {} \;. EXAMPLES chmod -w nowrite makes file nowrite read-only. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
Chmod -R permission directory name For example, to set the permission to 755 recursively to /var/www/ diirectory execute the command. Rw-r--r-Using the – R switch. You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc.
Chmod permission directory name To change the permissions of a directory with its files and sub-directories recursively, we run:. If you want to change the permissions of only files located inside specific directory then you will need to apply conditional file permissions recursively. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
Chmod +x myfile - Gives everyone execute permission on myfile. Here I have a file named file.txt. The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method:.
The basic syntax includes using the find command to locate files/directories and then passing it on to chmod to set the permission:. Permission levels and types Each file and directory has three permission levels (user, group and other) and three types of permission (read, write and execute) in each level. -rw-r--r-- 1 john john 272 Mar 17 08:22 test.txt.
There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. To remove write permission from orgcht:. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. For example, to create a directory that the accountants in a company can access, first make the group accounts by typing the following:.
Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. Following are some examples:. Now, suppose the task is to add execute permission for owner/user, remove write permission but add execute permission to group, and remove all permissions from others.
Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. Cd /var/www/mydirectory find.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa). For example, consider the following example:.
Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. To turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the set-user-ID bit, set-group-ID bit, and sticky bit attributes. If a user is not specified, chmod will check the umask and the effect will be as if "a" was specified except bits that are set in the umask are not affected.
To Give permission to any file/directory you have to use “+” Symbol. Changing permission for directory and subdirectory recursively in Unix This is the most frequently used example of a chmod command where we want to provide permission to any directory and all contents inside that directory including files and subdirectories. If all your files and directories are under one parent directory then you can directly use chmod -R <dir_name> to assign the permission recursively.
First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission. You use the chmod command to set each of these permissions. No such file or directory Please repeat Steps 1 and 4-5 above.
Groupadd accounts If you don't have the correct permission to create a group, use sudo to gain extra privileges or use the su command to switch to an account with valid permissions. The syntax to modify the file and directory permission recursively:.

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog

Chmod Permission Denied Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Users And Groups Linode

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Linux Command Cheat Sheet

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
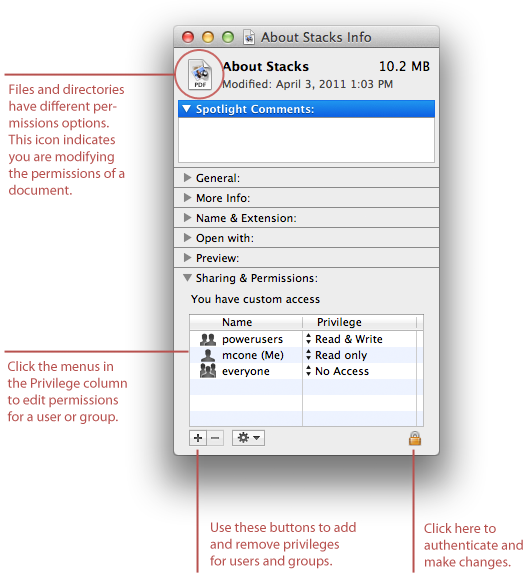
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Freebsd Find The Chmod Numerical Value For A File Or Directory Nixcraft
File And Directory Security Solaris Advanced User S Guide

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
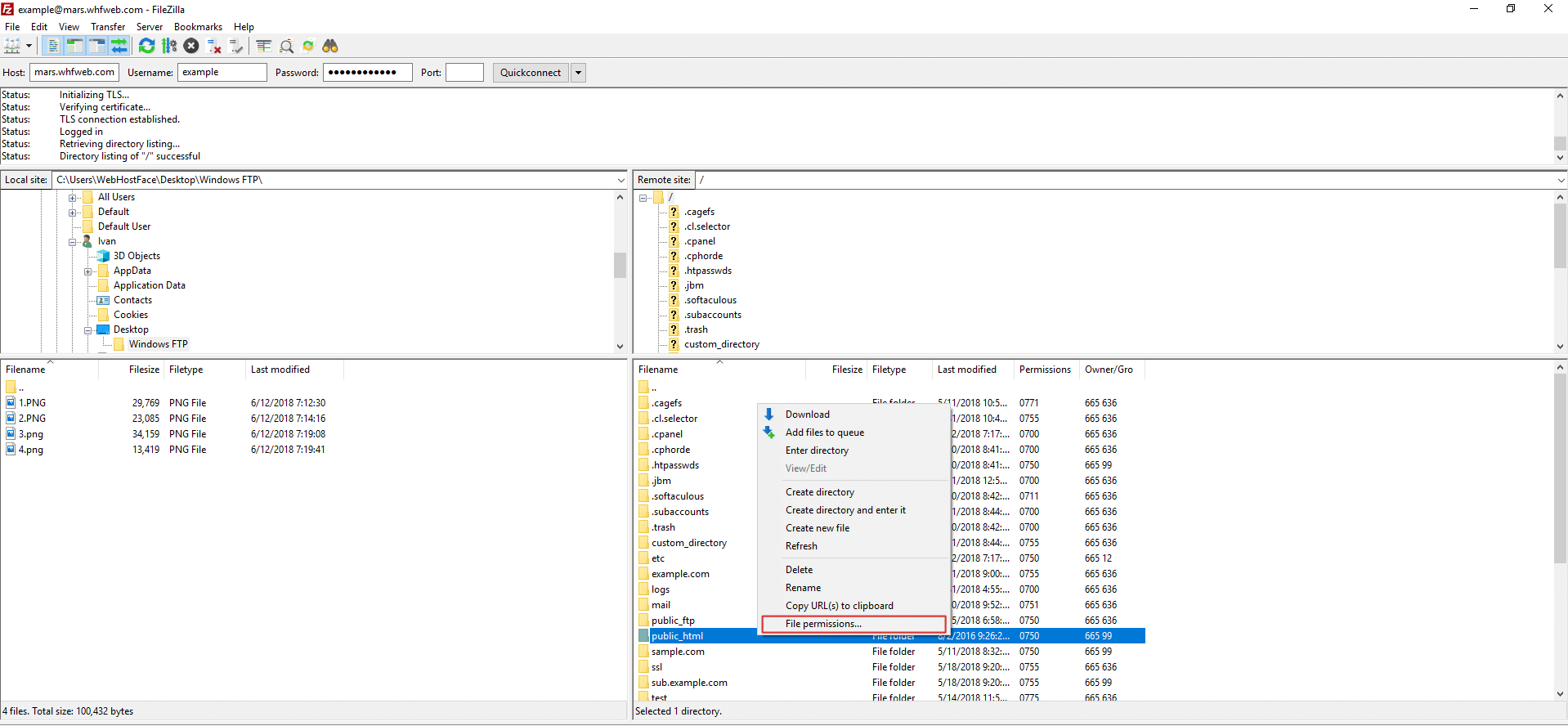
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

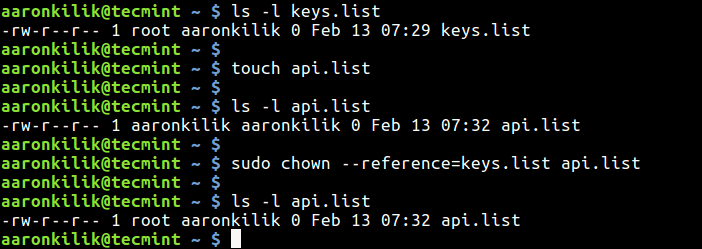
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau
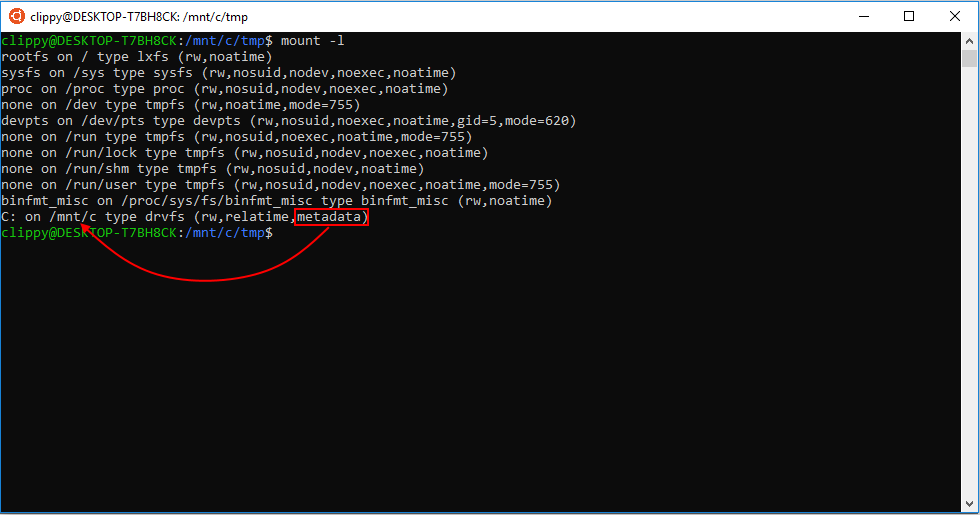
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Q Tbn 3aand9gcs G Rsxci 4gzclzblc809o4eg7fg Awkiw Usqp Cau

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

14 Permission And Modification Times

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Unix Permissions

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Give Write Access Chmod Unix

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Perl Chmod Command How To Set And Remove File And Directory Permissions Udemy Blog

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
Controlling File Permissions With Umask

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
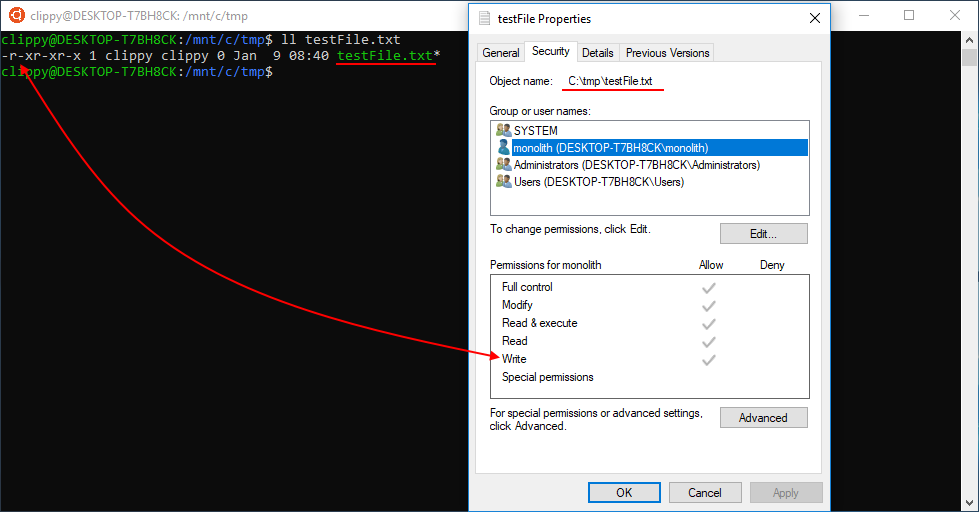
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
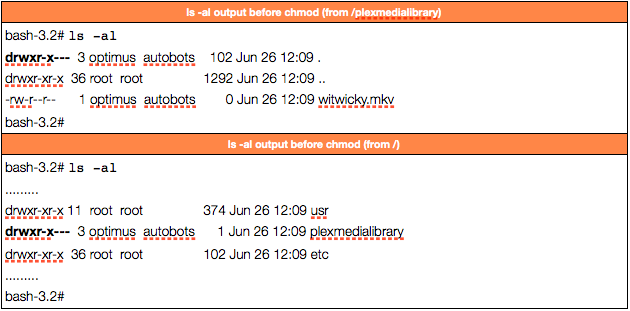
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
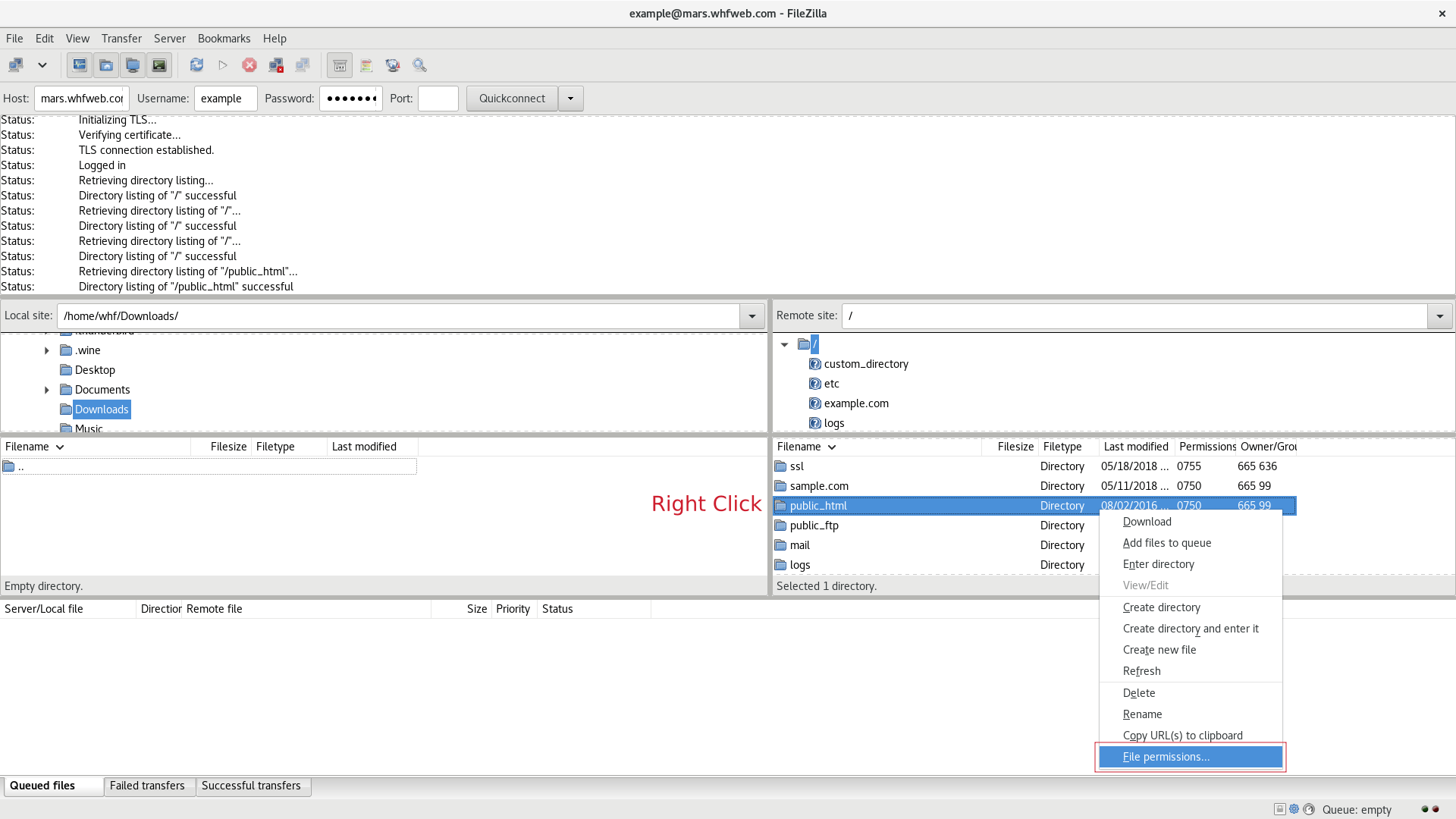
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
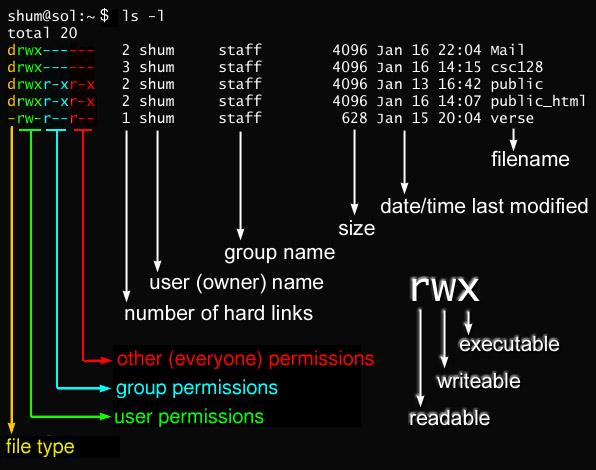
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
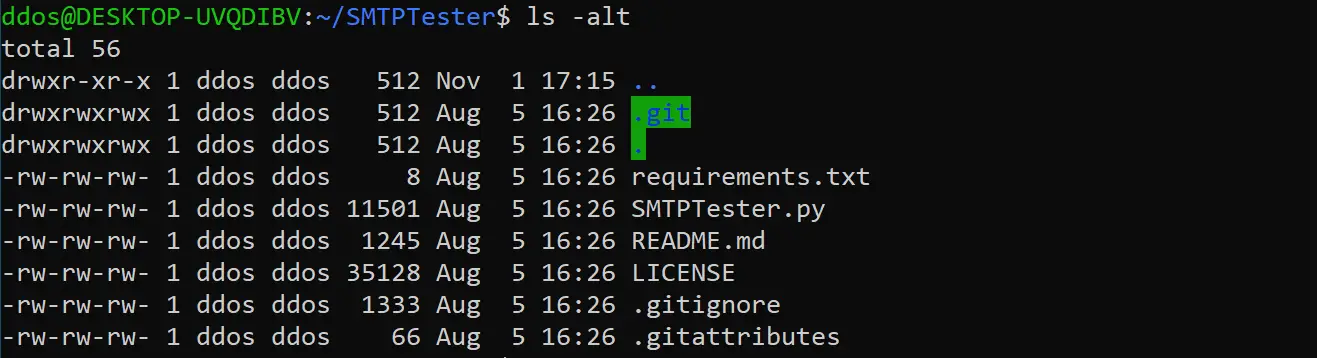
How To Change File Directory Permission In Linux Infotech News
How To Create A Read Only File In Your Home Directory In Unix Quora

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
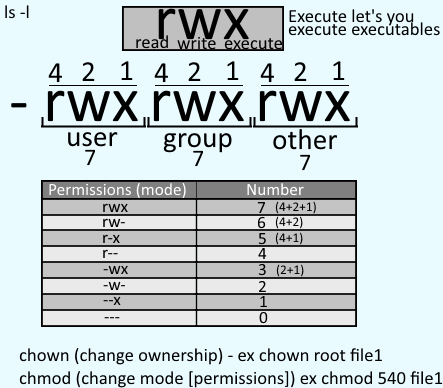
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Unix Tutorial Five

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Changing Permissions In Linux System Dev
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Chmod Wikipedia

Chmod Command

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Basic Chmod Examples



