Chmod Octal Command In Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Chmod Linuxconfig Org

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.

Chmod octal command in linux. # chmod 0761 file To setup a file readable by anyone and writable by the owner only:. $ ls -l sample.sh -rwx-rw-r-- 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 03:12 sample.sh. The request is filtered by the umask.
In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
Chmod options… Octal mode file Or:. Chmod options… Mode , mode… File Or:. This document describes the GNU / Linux version of chmod.
Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. Chmod stands for change mode. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions.
How to check chmod command version. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which.
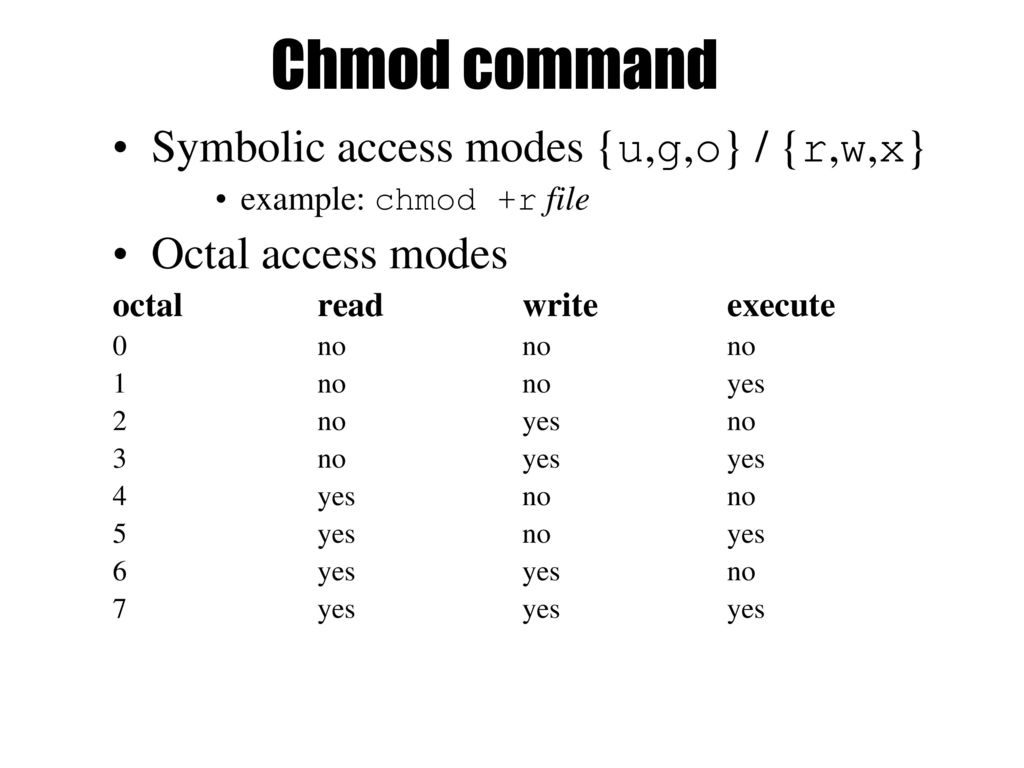
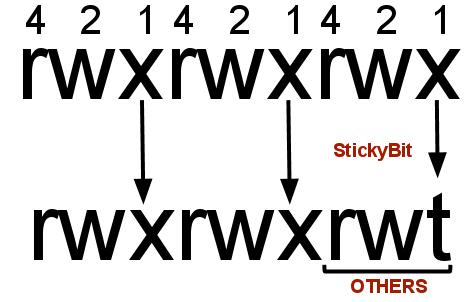
The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and sticky (1) attributes. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1.
The basic syntax is:. # chmod 755 test.txt # ls -l test.txt-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root Jun 17 12:01 test2.txt Changing permissions on a directory. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
The first octal digit sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits (see this article for more details on setuid/setgid). It also allows to change the file permission recursively to configure multiple files and sub-directories using a single command. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g.
Chmod -R a+rwx,o-rwx folder_name. Informative knowledge is provided with the help of The Linux Command-line as refrence/source. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. The command is usually used together with a set of octal notations or alphabetical characters to change file permissions.
Chmod has two operating modes:. Verbose Changes Silent Default. This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options.
Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed). # chmod 644 file To setup a file readable/executable by everyone and writable by the owner only:. Chmod command is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode which might be a set of octal characters or a set of alphabetical characters.
On Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, new files are created with a default set of permissions.Specifically, a new file's permissions may be restricted in a specific way by applying a permissions "mask" called the umask.The umask command is used to set this mask, or to show you its current value. That’s why a unix admins will say stuff like mode 755 and the bits magically. It takes the following syntax:.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers. Syntax umask -S maskOptions.
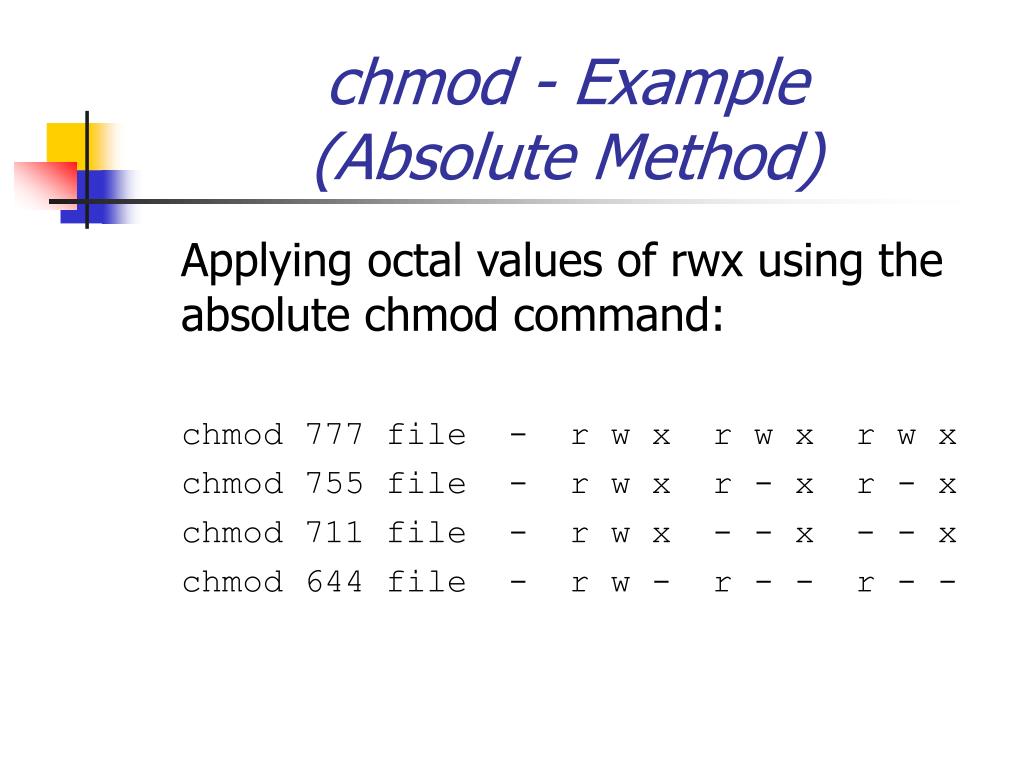
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. Please note that chmod 777 filename is the equivalent of chmod 0777 filename in this example. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1).
Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Only the object owner, superuser or root account can change the permissions of a file/folder.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use chmod recursively and change file permission on Linux. – C, — changes is similar to — verbose, but only displays results when there are changes. The chmod (change mode) command controls file permissions for the owner, group, and all other users who are neither the owner nor part of the group associated with the file.
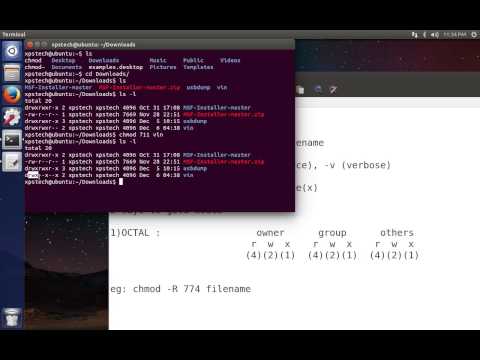
The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Chmod -R 770 folder_name. As you can see from below output current chmod version is 8.22.
Permission levels and types. To setup file permission 761 you need to use chmod command as follows:. Select the permissions you require below.
If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
How does chmod work?. This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work. This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used.
Chmod options… — Reference = reference file Change the mode of each file to the specified value. Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system. Recursive Preserve-Root Reference File.
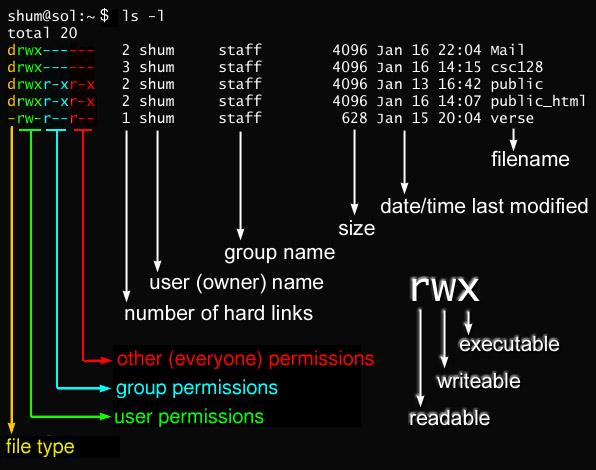
So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols. This command is used for changing the mode of access. It can further.
40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux. To use chmod, you need to know about access modes.Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine exactly who can. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux’s chmod command. The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files.
The string rwxr-xr-x represents the permissions of this file. In my previous blog post I discussed how Linux file permissions work, and now I am going to discuss how to change permissions using chmod. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. If you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks:. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE….
Chmod +rwx file_name chmod 777 file_name And. Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. Chmod Linux Command – chmod ใช้ในการเปลี่ยนสิทธิ์ในการอ่าน, เขียน และ execute file หรือ folder แบ่งเป็นสิทธิ์ของ file owner, group owner, other user ซึ่งคำสั่งจะถูกแปลงจากเลขฐาน 8 ในการระบุ.
Chmod Permissions for chmod 770. Understanding of attribute which can be out put by ls-l:. OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command:.
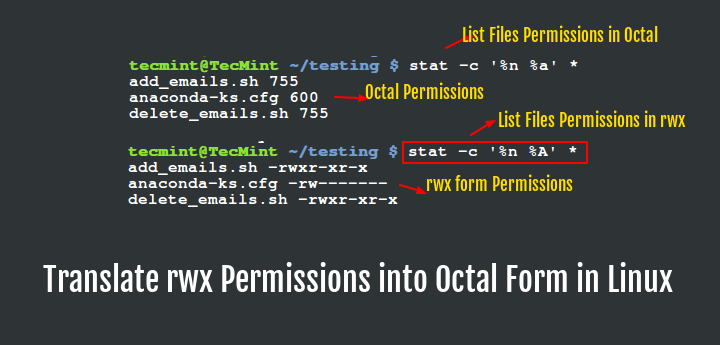
This manual page documents the GNU version of chmod. To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls -l command as shown below:. Basic “chmod” Command examples in Linux.
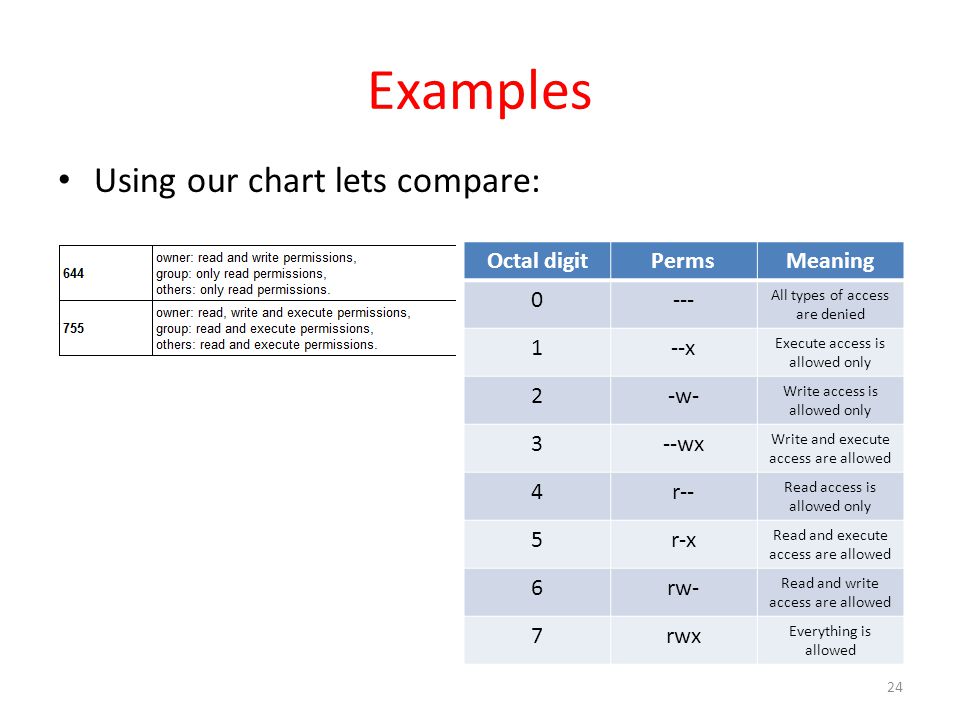
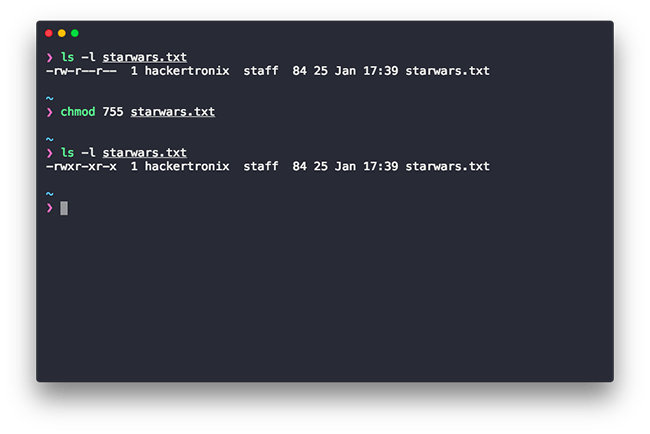
Conclusion # You successfully learned how to use chmod command to set or change the file and directories permissions using either the symbolic or numeric mode. The chmod command can be used with octals (as. Chmod Octal Permission for file File/Directory Name e.g – a) If we want to change the permission as per diagram 2.1 we need to execute below command $ chmod 777 filename.txt $ ls -l filename.txt-rwxrwxrwx 1 chandan chandan 0 Jun 5 21:48 filename.txt.
In this 2-minute Linux tip, we’re going to look at the chmod command – the command for. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions.
# chmod 755 file You can change permissions for all files and directories within a directory. Extra chmod command options. Chmod is the command used to change the permissions of an object, and is short for “CHange MODe”.
You can change file permissions in this format:. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. For example, to set the permissions of filename to -rw-r--r--you could run the command:.
The output of this command will look something like this:. To view these online, enter. We have already described the Linux file permissions.
Octal 2 means to set group ID on the file. Syntax to change the permission in Octal Notation:. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.
It is also used to change special mode flags. It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Chmod command is used in two ways :. How to use chmod?.
The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permis- sions of the pointed-to file. To set the permissions of a file or directory using numeric modes, simply use the format:.
Where OCTAL-MODE is the octal form of the permissions. Hence Following work same like:. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command sets the permissions of files or directories.
Because unix was written a long time ago (in computer years, at least), people who used it were fairly geeky and thought nothing of slinging binary, octal and hex around. Using Numeric Modes With Chmod. Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories.
Umask is a 3 digit octal number. If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod --version command as shown below. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
Assuming 444 (r–r–r–) permissions on the test.txt file, we change it to 755 (rwx-r-x-r-x). Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. Chmod OCTAL-MODE FILE… – Here we use the base command without any options.
The chmod command can set permissions in both octal (e.g., 755, 644, etc.) and symbolic (e.g., u+rwx, g-rwx, o=rw) formatting. Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. Chmod command in Linux What is chmod?.
The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. How to use chmod?. Chmod (Ch ange Mod e) is a command line utility in Unix, Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner, group and others.
Hi, this is Sandra Henry-Stocker, author of the “Unix as a Second Language” blog on NetworkWorld. First of all it is very essential to know about ugo and rwx manner:. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions.
Setuid Setgid Sticky Bit.

Common Bash Commands

What Are User And Group Permissions 荷树栋 博客园

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Read Write Access Chmod 775

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Find Unix Linux Command W3ki

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

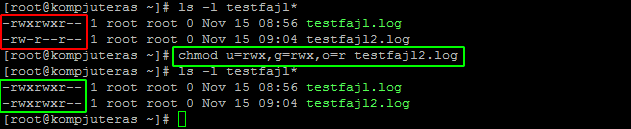
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

File Permissions How To Use Chmod Command Youtube

Linux Cheat Sheet Commands Pdf Download Printable
Chmod 0400 Means

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks

Solved B To Remove Myfile Ordinary File From The Paren Chegg Com

Linux And Unix Chmod Command Knowledge Hub

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Cheat Sheet
Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Changing Linux Files Directory Permissions Dba Genesis Support

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
Translate Rwx Permissions Into Octal Format In Linux

Unix Command Line Basics 4 Permissions Lennoxfiles

Linux Tutorial How To Use Chmod To Update File And Directory Permissions Steemit

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmtof5oge8os R2lzc9s8y8xkmcm3kyhtt M Kqujtci7flb3h Usqp Cau

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How To Get Octal File Permissions On Linux Unix Command Line Nixcraft

Chmod File Permission And The Octal Notation Netseed

Chmod In Unix C Programs

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Unix Permissions
Github Fed Command Line Cheatsheet Unix Command Line Cheatsheet

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod 0400 Means

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather

File Security

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Linux Commands For The Intermediate Users Techlila
What Is A Sticky Bit And How To Set It In Linux The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Umask Wikipedia

How To Get Octal File Permissions From Command Line In Mac Os Osxdaily

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Added By Galpeartech Instagram Post Update And Refresh Your Linux Knowledge Follow Galpeartech Chmod Is One Of The Most Important Command Which You Can Use To Change The Permission In Linux System

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Chmod And Chown Must Know Linux Commands

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Designlinux

14 Permission And Modification Times

Basic Linux Commands Ubuntu

How To Change Permissions In Linux

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube
Linux Chmod Tips
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod Wikipedia

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux Permissions Pluralsight



